What is CBD?
CBD (Cannabidiol) is from industrial hemp, specifically the cannabis sativa strain. Straight from the source, it is anti-fungal, anti- bacterial, anti-viral and anti inflammatory. Unlike its common counterpart THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), CBD does not have any psychoactive effects. There are many phytocannabinoids within the hemp plant such as CBDA, CBG, CBGA and more. CBD encompasses their wellness abilities and so much more.
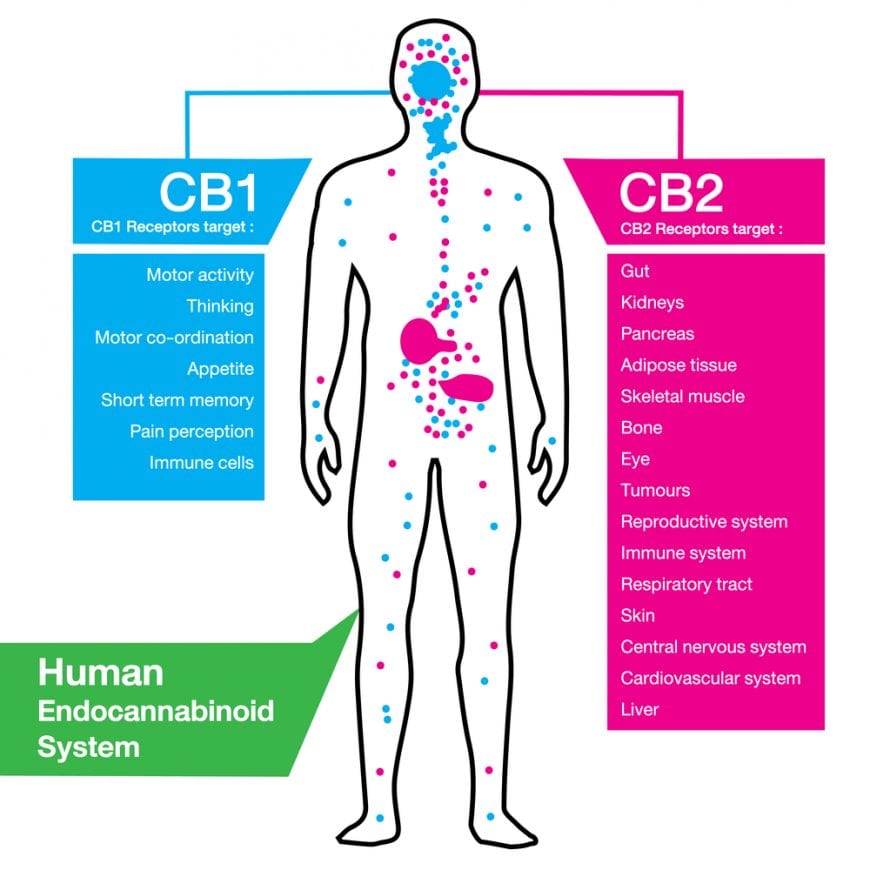
The body has two different CB (cannabinoid) receptors. CB-1 is found in the peripheral nervous system and assists with the functions of the immune system. CB-2 is found primarily in the immune system, digestive system (gastrointestinal tract), and many of the body’s major organs.
Whether CBD is applied topically, ingested or inhaled, it enters the body and activates the CB receptors. This helps the body become balanced and improves functionality.
How does CBD Work?
CBD is an adaptogen, and travels where there are imbalances within the body. For example, if someone has emotional imbalances that increases their stress levels, CBD adapts and assists the body with the imbalance, naturally. This is possible with the endocannabinoid system.
This is why CBD can assist the body with many ailments. If there is an imbalance within the body causing inflammation, stress, mood imbalances, or other issues, CBD naturally helps re-balance the body to a homeostasis state.
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
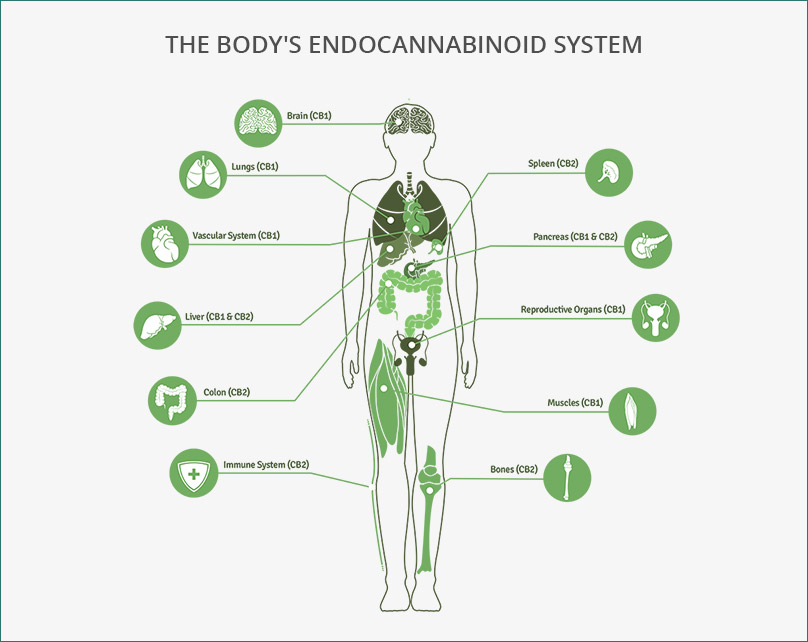
The Endocannabinoid System1 (ECS) plays a vital role in the Central Nervous System (CNS) in its development, synaptic plasticity, and more. It is responsible for maintaining homeostasis in the body. The endocannabinoid system regulates not only the central and peripheral mechanisms of food intake but also lipids synthesis and turnover in the liver and adipose tissue as well as glucose metabolism in muscle cells2 within the endocannabinoid system are cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors.
What are CB Receptors?
CB receptors are G-proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells.3 CB-1 is found in the peripheral nervous system and assists with the functions of the immune system and also found in brain areas related to the perception of emotions.4 These receptors are important for the regulation of mood imbalances and have also been identified as a possible target for the pharmacotherapy of pain and inflammation, other central nervous system disorders, nausea, cardiovascular and respiratory disorders, eye disorders, gastrointestinal disorders, and musculoskeletal disorders.5
CB-2 is found primarily in the immune system, digestive system (gastrointestinal tract), and many of the body’s major organs. CB2 receptors have been shown to be anti-inflammatory and effective against inflammatory, neuropathic, and post-surgical pain, in addition to chemical-(capsaicin and formalin) induced pain.6
CBD also assists with cell life by working with a fatty acid, Anandamide.
Anandamide
Anandamide is an endocannabinoid belonging to the class of fatty acid amides.7 Anandamide synthesizes in areas of the brain where memory, motivation, superior cognitive processes and movement control are managed. In this way, it influences physiological systems such as pain, appetite regulation and pleasure.8
The Anandamide protein also assists with the life cycle of cells in the body. The human body is created of cells. There is an entire process of cellular life which includes the death of a cell. In some instances when a cell is mutated and does not die, it passes along the mutation that keeps cells from dying, creating tumors and growths within the body. The endocannabinoid anandamide (AEA) is shown to induce apoptotic body’s formation and DNA fragmentation, hallmarks of programmed cell death.9 Meaning, it promotes a healthy cell life cycle.
1https://www.cannainsider.com/reviews/the-endocannabinoid-system/
2 “The role of the endocannabinoid system in the regulation of – NCBI.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17369778
3 “G protein – Wikipedia.” https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein
4 Howlett, A. C., Breivogel, C. S., Childers, S.R., Deadwyler, S.A., Hampson, R.E. and Porrino, L.J. 2004. Cannabinoid physiology and pharmacology: 30
years of progress. Neuropharmacology 47: 345-358.
5 Pacher, P., Batkai, S. and Kunos, G. 2006. Endocannabinoid System as an Emerging Target of Pharmacotherapy. Pharmacological Reviews 58: 389-462
6 Malan TP, Ibrahim MM, Deng HF, Liu Q, Mata HP, Vanderah T, Porreca F, Makriyannis A. CB2 cannabinoid receptor-mediated peripheral antinociception. Pain. 2001a; 93:239–245. [PubMed:11514083]
7 D. Matthew Walentiny et alt. The endogenous cannabinoid anandamide shares discriminative stimulus effects with ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol in fatty acid amide hydrolase knockout mice. European Journal of Pharmacology Volume 656, Issues 1–3, 10 April 2011, Pages 63–67
8 https://www.kalapa-clinic.com/en/what-is-anandamide/#_ftn1
9“Anandamide Induces Apoptosis in Human Cells via Vanilloid Receptors.” 13 Oct. 2000, http://www.jbc.org/content/275/41/31938.full.
